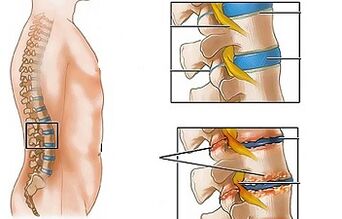
Lumbar osteochondrosis is a chronic disease that is resulting from a degenerative-dynist process in intervertebral discs.The disease is widespread and is affected in most cases at the age of 25-40.
Back pain statistics show that every other adult is experienced at least once in the life of an adult, while in 95% of cases, the osteochondrosis of the spine is a consequence.
Lumbar osteochondrosis patients with severe, persistent pain and other manifestations are considered temporarily disabled.If their condition does not improve within four months, the issue of creating a disability group will be resolved.
Lumbar osteochondrosis is a serious medical and social problem, as the disease is primarily affected by people of the most appropriate age and, in addition to treatment, can cause the formation of intervertebrate disk hernia.
Reasons and risk factors
Factors prone to lumbar osteochondrosis:
- disorders of the spine structure;
- Lumbalization is the congenital pathology of the spine, characterized by the separation of the first vertebra from sacrum and the sixth (supplementary) lumbar transformation;
- Sacralization is a congenital pathology in which the fifth lumbar vertebra is fed with the sacrum;
- asymmetric location of the joint cracks of the intervertebral joints;
- abnormal narrowing of the spinal canal;
- Reflected spondiogenic pain (somatic and muscle);
- obesity;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- longer vibration;
- systematic physical strain;
- smoking.
In combination with one or more risk factors, harmful statodynamic loads lead to a change in the physiological properties of the fibrous disk's coat core, play a shocking role and provide the mobility of the spinal column.This process is based on depolymerization of polysaccharides, which leads to the loss of moisture with the tissue of the jet.As a result, the coat core and, consequently, the fibrous disk lose its elastic properties.Further mechanical loads provoke the protrusion of the fibrous ring, which has lost flexibility.This phenomenon is called protrusion.The cracks appear in the fibrous core through which the fragments of the jacket cores (prolaps, the intervertebral disk) fall out.
Long compression of the nerve roots in the nerve roots of some organs in the abdominal cavity leads to a deterioration of their operation over time.
The instability of the spine segment is accompanied by reactive changes in adjacent vertebrae, intervertebral joints and concomitant spondil -arthrosis.Significant muscle contraction, such as physical activity, leads to the development of radicular syndrome in the background of physical activity, and nerve roots.
Otteophytes may be another cause of pain and neurological symptoms in lumbar osteochondrosis - bones outgrowths on the vertebrae processes and body that cause Royshold syndrome or compression myelopathy (spinal compression).
The forms of illness
Depending on which structures is involved in the pathological process, lumbar osteochondrosis is clinically manifested with the following syndromes:
- Reflex- lumbalgia, lumboichachalia, lumbago;Develop the background of the reflex surge of the back muscles;
- compression (spine, vascular system, radicular)- Their development leads to compression (compression) of spinal cord, blood vessels or nerve roots.Examples of lumbosacral radiculitis, radiccy.
Symptoms of lumbar osteochondrosis
In the case of lumbar osteochondrosis, the symptoms are determined by the fact that structures are involved in the pathological process.
Lumbago occurs under the influence of hypothermia or physical surge and sometimes for no obvious reason.The pain suddenly appears and fires.Hyp, cough, body turns, physical effort, seat, standing, walking increases.In the main situation, the pain is significantly weakened.Sensitivity and reflexes remain, and the amount of movement of the lumbar region is reduced.
Observed when palpation:
- pain in the lumbar region;
- Paravertebral muscles are cramps;
- The flattening of lumbar lordosis, which is often combined with skoliosis.
The tension syndrome of the nerve roots is negative with the groin.When lifting the straight leg, patients note the increase in the lower back and not their appearance in the elongated lower limb.
Often, lumbar osteochondrosis is repeatedly found in pain, which are increasingly intense and long.
In lumbalia, the clinical picture is similar to a lumbago, but the intensity of the pain occurs within a few days.
Lumbar shaped, patients complain at the lower back, which radiates to one or both lower limbs.The pain spreads on the back of the buttocks and thighs and never reaches the leg.
Vasomotor disorders are typical of lumbar shaking:
- changes in the skin temperature and color of the lower limbs;
- feeling of heat or cooling;
- Violation of blood supply.
The formation of lumbar compression syndromes is clinically indicated by the following symptoms:
- Dermatomic Gipalgesia;
- shooting;
- weakening or total loss of deep reflexes;
- Peripheral paresis.
In compression syndromes, the pain increases when the body is overthrown, sneezing and coughing.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of lumbar osteochondrosis is based on a clinical picture of disease, laboratory and instrumental research methods.
In blood tests, lumbar osteochondrosis can be noted:
- decrease in calcium concentration;
- ESR growth;
- Increase the level of alkaline phosphatase.
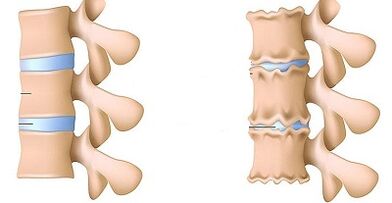
In diagnosis of lumbar osteochondrosis, radiological examination of the spine is of great importance.
Long compression of the nerve roots in the nerve roots of some organs in the abdominal cavity leads to a deterioration of their operation over time.
X -Ray properties that confirm the diagnosis:
- Change in the configuration of the affected segment;
- Pseudospondylastez (shift of related spinal bodies);
- Deformation of closing discs;
- flatness of the intervertebral disc;
- The uneven height of the intervertebral disk (symptom of the spacer), which is associated with asymmetric muscle tone.
In the presence of indications in the diagnosis of lumbar osteochondrosis:
- Myelography, calculated or magnetic rejection tomography - requires permanent symptoms, neurological deficiency;
- Scintigraphy (examination of the accumulation of phosphorus bone system, molten technology-99)-is performed in case of suspicion of a tumor or infectious process.
Differential diagnosis of lumbar osteochondrosis is done with the following diseases:
- Spondylolistz;
- Disgormonal spondilopathy;
- Ankylosing spondylitis (ankylosing spondylitis);
- Infectious processes (discs inflammation, spine osteomyelitis);
- non -plastic processes (primary tumors of the spine or metastatic injuries);
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- Deformation of osteoarthrosis of the hip joint;
- Reflected pains (internal organs and large blood vessels).
Treating lumbar osteochondrosis
In the case of lumbar osteochondrosis, the following treatment tactics are generally adhered to:
- bed rest for 2-3 days;
- adhesion of the affected segment of the spine;
- strengthening the muscles of the back and abdominal press (creating the muscle linker so called);
- Effect on pathological myofascial and myotonic processes.
Lumbago occurs under the influence of hypothermia or physical surge and sometimes for no obvious reason.
In most cases, we take conservative treatment of lumbar osteochondrosis, including the following measures:
- muscle infiltration by solving local anesthetics;
- Gender -steroid anti -inflammatory drugs;
- receiving desensitic agents;
- vitamin therapy;
- receiving sedatives and antidepressants;
- Manual therapy, massage;
- physiotherapy physical education;
- acupuncture;
- Postisometric relaxation.
Absolute indications for the surgical treatment of lumbar osteochondrosis:
- acute or subacute compression of the spinal cord;
- Development of horse tail syndrome, characterized by the impaired function of pelvic organs, sensitive and motor disorders.
Medical gymnastics for lumbar osteochondrosis
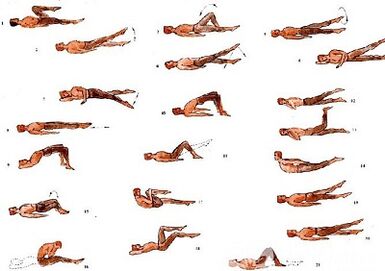
It plays an important role in the treatment of lumbar osteochondrosis complex physiotherapy.Regular classes allow the normalization of the muscle tone of the paravertebral muscles, to improve the metabolic processes of tissues affected by the pathological process, and to form a well -developed muscle coating that keeps the spine in the right position, remove excessive static loads.
In order to ensure that gymnastics with lumbar osteochondrosis have the greatest impact on following the following principles:
- the regularity of classes;
- gradual increase in physical effort intensity;
- To avoid overtime during the clock.
Physical education should be involved in the management of an experienced instructor who selects the most effective exercises for a particular patient and will check the correctness of the implementation.
Back pain statistics show that every other adult is experienced at least once in the life of an adult, while in 95% of cases, the osteochondrosis of the spine is a consequence.
In addition to the classes with the instructor, you must perform the morning gymnastics complex daily, which includes special exercises with lumbar osteochondrosis.
- Relaxation and contraction of the abdominal muscles.The starting position is, the legs are on the shoulders, the body's hands are lowered.Make a smooth breath and relax the muscles of the front abdominal wall.During exhalation, pull yourself as much as possible, tightening the press muscles.The exercise should be repeated before light fatigue appears.
- The movement of the head by bending the spine.The starting position of the knee, resting from the back on the floor, is straight.Slowly lift your head and bend your back.To pull in this position for a few seconds and then return to its original position smoothly.Repeat at least 10-12 times.
- "Pendulum".The starting position on the back, lying along the body, is bent at the right angles of the knees and hip joints.Rotate the legs to the right and left with swingy pendulum movements, trying to get the floor.However, the blades are not broken from the floor.
- "Ship".The starting position on the stomach, the hands are extended in advance.Torn the upper body and legs from the floor, leaning from the back.To take 5-6 seconds in this situation and slowly return to the starting position.Do 10 times.
Possible consequences and complications
The main complications of lumbar osteochondrosis are as follows:
- the formation of intervertebral hernia;
- Vegetovascular dystonia;
- Spondylolis, spondylolistz;
- osteophytosis;
- spondylarthrosis;
- Stenosis of the spinal canal, which can lead to spinal compression and lasting loss of working capacity and reducing quality of life.
Long compression of the nerve roots in the nerve roots of some organs in the abdominal cavity leads to a deterioration of their operation over time.As a result, patients' intestinal dysfunctions (constipation, diarrhea, phenelia) and pelvic organs (urinary disorders, erectile dysfunction, frigidity, infertility) have.
Forecast
Lumbar osteochondrosis pain syndrome is in the form of remission and aggravations.The Lumbago lasts 10-15 days, then the patient's condition improves and the pain disappears.Secondary secondary diseases can be distinguished by favorable results.Often, lumbar osteochondrosis is repeatedly found in pain, which are increasingly intense and long.
It plays an important role in the treatment of lumbar osteochondrosis complex physiotherapy.
Lumbar osteochondrosis patients with severe, persistent pain and other manifestations are considered temporarily disabled.If their condition does not improve within four months, the issue of creating a disability group will be resolved.
Prevention
Preventing the development of spine osteochondrosis as follows:
- Denial of smoking;
- Normalization of body weight;
- general physical condition, improvement of active lifestyle;
- Avoiding provocation conditions (weight lifting, sharp movements, turns, tilts).


















































